EMERALD SUN: an integrated large-scale learning and discovery system for education and research in machine learning
(Michalski, Kaufman, Bloedorn)
This project concerns the development and maintenance of an integrated system for machine learning and discovery, EMERALD, that serves as a tool for education and research in machine learning and cognitive modeling of learning processes. The system was regularly used in teaching the course INFT 811: “Principles of Machine Learning and Inference” and occasionally some other courses.

This figure presents the opening screen of the EMERALD system developed in the Machine Learning and Inference Laboratory. The EMERALD system (Experimental Machine Example-based Reasoning and Learning Disciple) integrate s five modules (“robots”) each displaying a capability for some form of learning or discovery. The Emerald is based on an earlier system, ILIAN, which toured all major U.S. Museums of Science.
| AQ learns general decision rules from examples of different classes of correct or incorrect decisions made by experts. An example of the program performance employs little robots like these: |  |
| INDUCE learns structural descriptions of groups of objects, and determines important distinctions between the groups. An example of INDUCE performance uses little trains like these: | |
| CLUSTER creates meaningful categories and classifications of given entities, and formulates descriptions of these created categories. One of the examples illustrating CLUSTER performance involves the clustering of various geometric objects into different classes as shown here. | 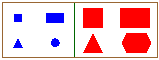 |
| SPARC predicts possible future objects or events by discovering rules characterizing the sequence of objects or events observed so far. One of the examples illustrating SPARC performance involves the prediction of a sequence of cards in the game ELEUSIS. | |
| ABACUS conducts experiments, collects data, discovers mathematical and logical descriptions of data, and then uses these descriptions for predicting the behavior of some phenomenon. One of the experiments illustrating ABACUS involves the discovery of a law characterizing bodies falling through different media. | 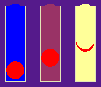 |
Each module is represented by a robot figure and employs a different voice (through a voice synthesizer) for communicating with the user.
An earlier and smaller version of the system, called ILLIAN, was a part of the exhibition “Robots and Beyond: The Age of Intelligent Machines,” organized by a consortium of eight U.S. Museums of Science (Boston, Charlotte, Fort Worth, Los Angeles, Seattle, Chicago, Minneapolis and Columbus). Support for the development of the exhibit version was provided in part by the Boston Museum of Science, Digital Equipment Corporation, and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The system was seen by few hundred thousand people.
EMERALD is the first system of its kind ever built, which integrates several learning capabilities with natural language processing, voice communication, and a highly user-oriented graphical interface. It enables users to experiment on-line with various learning and discovery programs under a unified control, and to use predefined objects to set different learning tasks for the system. EMERALD was developed under the direction of Professor R.S. Michalski in collaboration with his students and associates. The system has recently been adapted for SUN workstations, and used in teaching machine learning.
EMERALD has been distributed to a number of U.S. and European universities and organizations.
Although EMERALD modules are demonstrated in the context of certain predefined classes of problems, they are not specifically oriented toward these problems and objects. These modules are domain-independent programs that have already been used or have a potential to be used for concept learning and discovering regularities in such fields as medicine, agriculture, engineering, biology, chemistry, plant control, financial decisions, air traffic control, computer vision and intelligent robots.
Selected References
Kaufman K. A and Michalski, R.S., “EMERALD 2: An Integrated System of Machine Learning and Discovery Programs for Education and Research, Programmer’s Guide for the Sun Workstation (Updated Edition),” Reports of the Machine Learning and Inference Laboratory, MLI 97-9, George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, 1997.
Kaufman K.A. and Michalski, R.S., “EMERALD 2: An Integrated System of Machine Learning and Discovery Programs for Education and Research, User’s Guide (Updated Edition),” Reports of the Machine Learning and Inference Laboratory, MLI 97-8, George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, 1997.
Kaufman, K.A. and Michalski, R.S., “EMERALD: An Integrated System of Machine Learning and Discovery Programs to Support Education and Experimental Research,” Reports of the Machine Learning and Inference Laboratory, MLI 93-10, School of Information Technology and Engineering, George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, September 1993.
For more references, see publications section.
